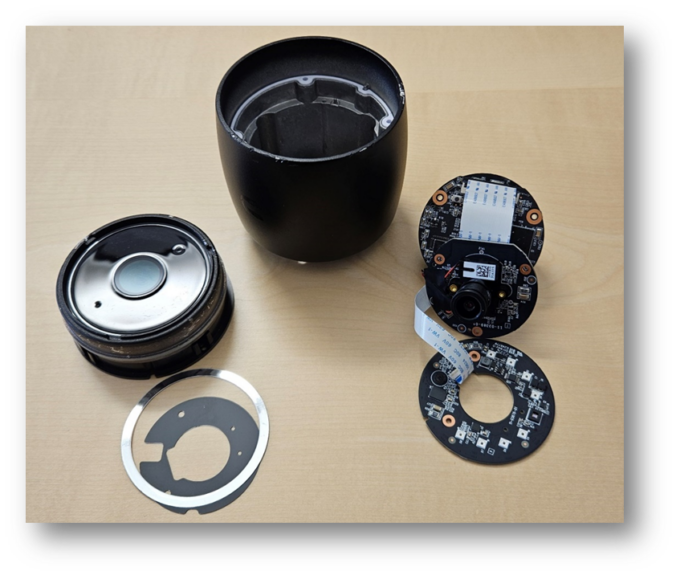
Introduction As you may know, Compass Security participated in the 2023 edition of the Pwn2Own contest in Toronto and was able to successfully compromise the Synology BC500 camera using a remote code execution vulnerability. If you missed this, head over to the blog post here https://blog.compass-security.com/2024/03/pwn2own-toronto-2023-part-1-how-it-all-started/ Unfortunately, the same vulnerability was also identified by other […]
Compass Security Blog
Offensive Defense
As a pentester you are sometimes thrown into projects where you have no idea where you are going to end up. This project was one of those where you were given a customer laptop and the aim was to “find something interesting”, perhaps a misconfiguration on the customer side. The problem was that the laptop […]
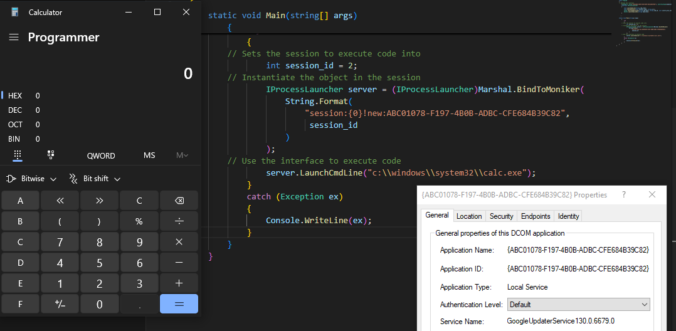
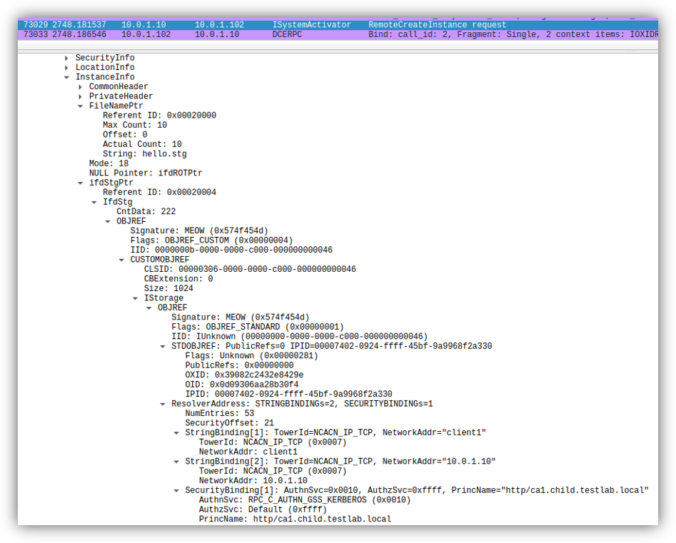
Once again, reading blogs and tweets from James Forshaw led me to wonder how things work. This time, I was working on DCOM for my last blog post and while reading about cross-session activation, I had trouble believing what I was reading.
Earlier this year, several security researchers published research about using DCOM to coerce Windows systems to authenticate to other systems. This can be misused to relay the authentication to NTLM or Kerberos, to AD CS over HTTP for instance. This sounds like a hot and complex topic. Let’s take a look back how this started […]
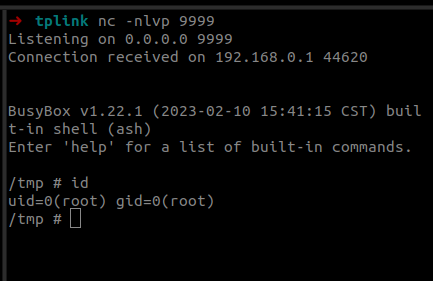
Last year we participated in the Pwn2Own 2023 Toronto competition and successfully exploited the Synology BC500 camera. The DEVCORE Internship Program team managed to exploit a bug in the TP-Link Omada Gigabit VPN Router. So I was naturally curious and wanted to figure out how difficult it would be to recreate that exploit having access only to a high-level bug description and the firmware.
At Compass Security, we recently launched our managed bug bounty service. We openly invite hunters to probe our publicly exposed services for vulnerabilities. In return for their valuable feedback, we offer monetary bounties up to CHF 5000. This blog posts presents an interesting vulnerability found by a hunter on the bug bounty program of our subsidiary, Hacking-Lab.
TL;DR An attacker is able to register new security keys (FIDO) or other authentication methods (TOTP, Email, Phone etc.) after a successful device code phishing attack. This allows an attacker to backdoor the account (FIDO) or perform the self-service password reset for the account with the newly registered sign-in methods. Microsoft deemed this not a vulnerability.
A journey into the discovery of privilege escalation vulnerabilities in the Lenovo Update process.
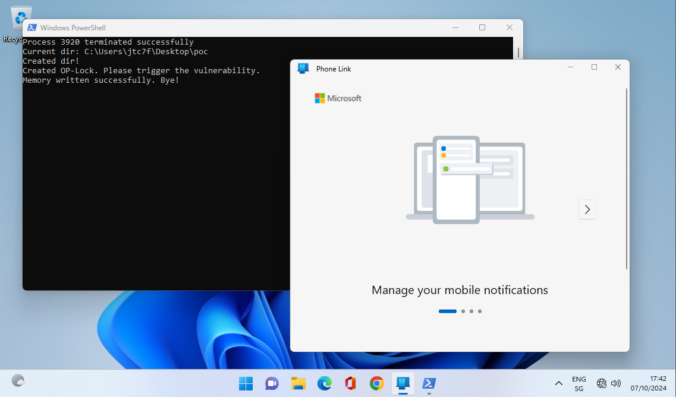
Passwordless products promise greater security and convenience by allowing users to log in to Windows systems with only their smartphone. But what is going on behind the scenes and how could a domain’s security stance be worsened by such a solution? In this post I will explain how these products are implemented and detail the vulnerabilities and weaknesses discovered in three tested products.
The end of the year is a good time to sit back and reflect for a moment on the past year. So let us take a look at the ten most common ways how I got Domain Admin privileges in our Active Directory penetration tests in 2021.
© 2025 Compass Security Blog